First, the basic concept of resistance and pressure reduction
1, what is resistance and pressure?
Resistor-to-capacitor step-down is a circuit that limits the maximum operating current by using capacitive reactance generated by a capacitor at a certain frequency of AC signal.
The capacitor actually plays a role in limiting the current and dynamically distributing the voltage across the capacitor and load.
2. What parts of the RC capacitor circuit consist of?
Resistor-capacity step-down circuit consists of buck module, rectifier module, voltage regulator module and filter module.

3, resistance and capacity buck basic design elements
When designing a circuit, it is necessary to determine the maximum operating current of the load and calculate the capacitance value of the capacitor through this current value so as to select an appropriate capacitor.
Here is the difference with the linear transformer power supply: The resistive-capacitive step-down power supply is selected by the load current; the linear transformer power supply is selected by the load voltage and power transformer.
Resistor-capacitor buck current calculation
Resistor-capacitor step-down circuit can be equivalently composed of a step-down capacitor C1 and a load resistor R1, and the resistor and the capacitor are connected in series.

The capacitive reactance of capacitor C1 is Zc=-j/wC=-j/2Ï€fC
Resistance of resistor R1 is Zr=R
The total equivalent impedance is Z=Zc+Zr=-j/2Ï€fC+R
So I=U/Z=U/(Zc+Zr)=U/(-j/2Ï€fC+R)

Because the resistive-capacity step-down power supply is only suitable for small-current circuits, the capacitance range of the selected capacitor is generally from 0.33 UF to 2.5 UF, so Zc is -1592 j to -9651 j. The equivalent load impedance Zr is about 200Ω, obviously there is |Zc|>>|Zr|, and the voltage drop of the input power supply voltage on the load is also much smaller than the voltage drop of the capacitor, so there are: Z≈Zc, vector The angle θ is close to 90°.
Therefore:
I=U/Z=U/Zc=U/(-j/2Ï€fC)
=220*2Ï€*f*C*j
=220*2Ï€*50*C*j
=j69000C
I=|I|∠90°, the current effective value I1=|I|=69000C. When the rectification mode uses half-wave rectification, I1=0.5|I|=34500C.
Design example
Known conditions: load operating current 15mA, operating voltage 5V. Seeking buck capacitance?
Using half-wave rectification, according to the formula I1=0.5|I|=34500C, C=0.43uF. Therefore, the capacitor of 0.47uF is used here, which in turn can verify that the supplied current I1=34500C=16.2mA, and the excess current flows through the regulator.
Resistance and pressure reduction advantages:
Small size; low cost.
Disadvantages of resistance and pressure reduction:
Non-isolated power supply, insecure;
Cannot be used for high power loads;
Not suitable for capacitive and inductive loads;
Not suitable for dynamic loads.
Second, the basic principle of resistance and pressure reduction
1, the principle of capacitor charging and discharging
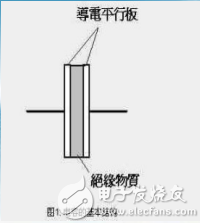
A capacitor is a passive device that stores energy in the form of an electric field. The nature of the charge-discharge process of the capacitor is the process of acquiring and releasing electrons from two conductive parallel plates.
Capacitor charging:
When the electric field strength E in the capacitor is less than the external power supply voltage U across the capacitor, the capacitor starts to charge. At this time, the positive electrode of the capacitor continuously loses electrons, and the negative electrode continuously gains electrons. The internal electric field E is continuously enhanced until it is equal to the external voltage U, and charging ends.
Capacitance discharge:
When the electric field strength E in the capacitor is greater than the external power supply voltage U across the capacitor, the capacitor begins to discharge. At this time, the positive electrode of the capacitor continuously gains electrons, the negative electrode continuously loses electrons, and the internal electric field E continuously weakens until it is equal to the external voltage U, and the discharge ends.
DC charge discharge process of capacitor


As shown in the above charging process, seek C1 voltage rushed to 1V time:
Since V0=0V, Vt=1V, V1=5V, R=10K, C=0.1uF, T=10000*0.1*0.000001*Ln(5/4)=223uS
Capacitor AC charge discharge process
DC charging and discharging of the capacitor is completed at once, and AC charging and discharging is a process that repeats itself.

Full-wave rectifier circuit


Half-wave rectifier circuit


The role of various components and options

F1: Fuse, for over-current protection, 400mA250V type.
RV1: varistor, from surge protection, generally use 10D471K model.
C1: Step-down capacitor, using a larger capacitive reactance to limit the total current in the circuit. Commonly used polyester capacitor (CL21), polypropylene capacitor (CBB21), safety capacitor (X2), the capacitance value depends on the load requirements, the greater the capacity of this capacitor, the more unsafe the circuit, in the design of this circuit, if the 220VAC power supply Under the capacity of more than 2.5uF, the capacity exceeds 4uF in the case of 110VAC power supply, because other circuits should be considered in order to give up resistance and voltage. The 0.56uF safety capacitor (X2) is used here to provide 19mA.
R2: Discharge resistance, providing a discharge circuit for the capacitor C1 after power off, to prevent the residual voltage on the C1 capacitor and the grid voltage from superimposing on the subsequent device to form a high-voltage shock and preventing the plug from being pulled out when the quick plugging of the power plug or the plug is bad. Contact with the human body causes injury to personnel. Generally, the time for the C1 voltage to decay to 37% after power off should be less than 1 second because T=RC*Ln[(V0-V1)/(Vt-V1)], so T=RC, R=t/C,R <1/C. Here, three 390K 0805 chip resistors (shared voltage and power) are used.
R1: Current-limiting resistor. This resistor is mainly used to prevent damage to the rectifier diode due to the high-voltage surge generated when the power is first applied and when the power plug or plug is rapidly connected or unplugged. When capacitor C2 is powered on for the first time, if it just hits the peak, C2 is short-circuited (first-order zero-state response) at the moment of power-on. At this time, AC power is directly applied to R1 and the rectifier. There is 220VAC*1.414=311VDC on R1. Instantaneous DC voltage, this voltage may be higher if C1 charge is not discharged at power up. Therefore, R1 should select a resistor with strong current-impact resistance and high-voltage resistance. The R1 resistor should not be too small or too large. The resistance is too small and the inrush current is large. The resistance is too large and the power consumption of the entire circuit increases. The peak current of the rectifier diode is generally relatively large, such as 1A400X series peak current is 50A, so generally take R1 resistance between 10-50Ω.
DZ1: Zener diode, select 1N4733, voltage regulator Vz is 5.1V. The maximum regulated current Iz of the DZ1 must be greater than the maximum charge and discharge current of the capacitor C1.
R5: RC filter with capacitors E1 and C2 reduces ripple.
D1: rectifier diode, half-wave rectification, use 1N4007.
D2: Rectifier diode, half-wave rectification, 1N4007.
E1: Electrolytic capacitor, which filters the regulated voltage, and provides power to the load during the half cycle of the power off. Before the next half cycle of power supply, E1 must ensure that the voltage provided for the load can not be attenuated too much, 1000uF25V model is used here. Since T=RC*Ln[(V0-V1)/(Vt-V1)]=10mS, the attenuated voltage Vt=4.8V.
C2: SMD capacitor, filtering effect, choose 0.1uF.
R6: Discharge resistance, providing a discharge circuit for E1 after power off, generally 5~10K.
R7: Equivalent load.
The main components of the picture
One time blow fuse

Resettable fuse

Varistors

Metallized Polyester Film Capacitors (CL21)

Metallized Polypropylene Capacitors (CBB21)

X2 safety capacitor (CBB62/MKP)

Third, resistance and pressure reduction applications
Resistor-capacitor buck is suitable for low-power and small-current loads due to its small size and low cost. Common applications include energy meters, low-power LED light drivers, small appliances, and thermostats.

LED light driver

Small appliances application
Fan controller

Electric heater controller

Coffee machine

Antenk mini usb:The small USB socket found on digital cameras, external hard drives, USB hubs and other equipment. Mini USB is much smaller than USB Type A and B but twice as thick as Micro USB (see illustration below).
MINI USB, also known as Mini USB, is a USB interface standard. USB is the abbreviation of universal serial bus in English, which means "universal serial bus" in Chinese. It is a technology developed for data transmission between PC and digital devices. Standard USB, MINIUSB and microusb have become the most common USB interfaces. Compared with standard USB, MINIUSB is smaller and suitable for small electronic devices such as mobile devices.
Mini USB is divided into a type, B type and ab type. Minib type 5pin interface is the most common interface. Due to its excellent anti misplug performance and small size, it is gaining the favor of many manufacturers. This interface is widely used in card readers, MP3, digital cameras and mobile hard disks.
Mini USB a, B connectors and their contacts (not drawn to scale) Mini USB Connector contact function
1 VBUS (4.4–5.25 V)
2 D−
3 D+
4 ID
5 grounding
The ID foot is only used in OTG function. The Mini USB interface is divided into mini-a, B and ab interfaces. If your system is only used as a slave, then use the B interface. The system controller will judge the level of the ID pin and determine what kind of device is inserted. If it is Gaoping, it is the B connector. At this time, the system will do slave mode. If the ID is low, it will be a interface. Then the system will use HNP dialogue protocol to decide which is the master and which is the slave
OTG is the abbreviation of on the go, that is, OTG technology is to realize the data transmission between devices without host. It is mainly used in the connection between different devices or mobile devices for data exchange. For example, the digital camera is directly connected to the printer, and through OTG technology, the USB port between two devices is connected to print out the photos taken immediately; the data in the digital camera can also be sent to the mobile hard disk of USB interface through OTG, so there is no need to carry expensive memory card or carry a portable computer for field operation.
Except for pin 4, other interface functions of Mini USB are the same as those of standard USB. The fourth needle becomes the ID, which is connected to the fifth needle on the mini-a, and can be suspended in the mini-b or connected to the fifth needle.
Mini USB
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkcon.com