The main features of the ZigBee network are low power consumption, low cost, low speed, support for a large number of nodes, support for multiple network topologies, low complexity, fast, reliable, and secure. The devices in the ZigBee network can be divided into three roles: Coordinator, Router, and EndDevice.
At the same time, ZigBee, as a short-range wireless communication technology, has a very strong applicability in the field of Internet of Things because its network can provide users with wireless data transmission functions conveniently.
What is zigbee?ZigBee is a low-power LAN protocol based on the IEEE802.15.4 standard. According to international standards, ZigBee technology is a short-range, low-power wireless communication technology. This name (also known as the Zigbee Protocol) comes from the bee's splay, because bees rely on flying and "zig" to shake the wings of the "dance" to convey the position of the pollen with the companion. That is to say, the bees rely on such a way to form a communication network in the group. It is characterized by close proximity, low complexity, self-organization, low power consumption, and low data rate. It is mainly suitable for use in the fields of automatic control and remote control and can be embedded in various devices.
In short, ZigBee is a cheap, low-power, short-range wireless networking communication technology. ZigBee is a wireless network protocol for low-speed short-distance transmission. The ZigBee protocol is a physical layer (PHY), a media access control layer (MAC), a transport layer (TL), a network layer (NWK), an application layer (APL), and the like from bottom to top. The physical layer and the media access control layer follow the IEEE 802.15.4 standard.
ZigBee protocol architectureThe layered architecture of the ZigBee protocol is defined according to the application and market needs. The architecture of the protocol is shown in Figure 1, where the physical layer (PHY) and the medium access control sub-layer (MAC) are Defined by the IEEE 802.15.4-2003 standard, the ZigBee Alliance defines the network layer (PHY) and application layer (APL) architecture based on this underlying protocol.
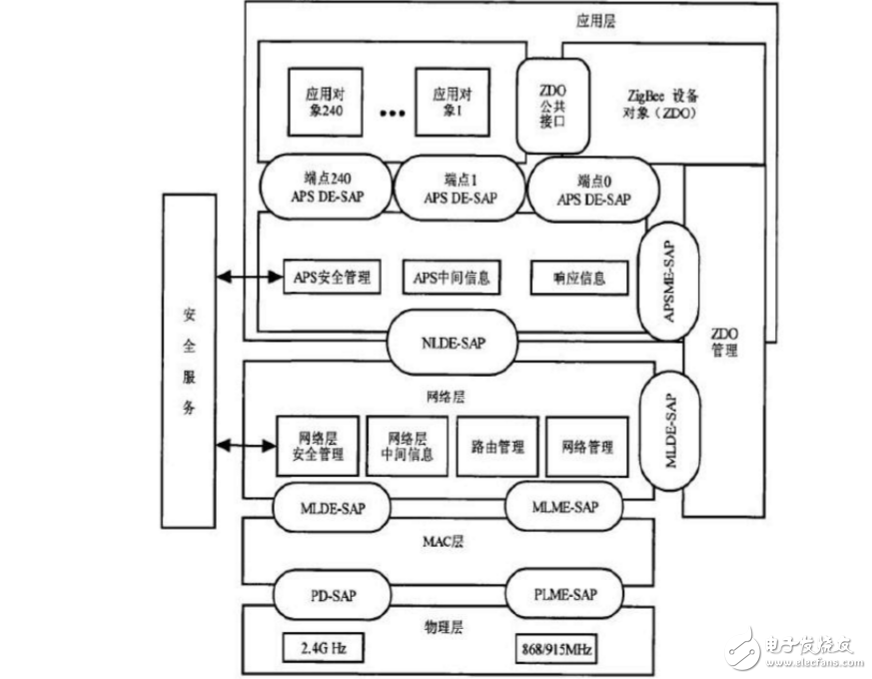
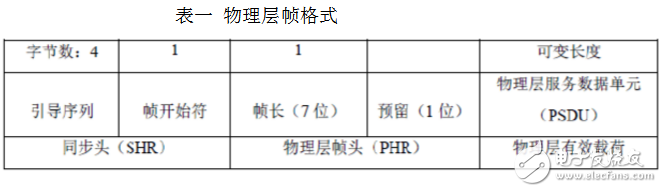
The physical layer defines two interfaces between it and the MAC layer: the data service interface PD-SAP and the management service interface PLME-SAP, where the PD-SAP interface also provides the corresponding data service for the physical layer, responsible for the secondary physical channel. The data is sent and received, and the PLME-SAP interface provides corresponding management services for the physical layer to maintain a database composed of physical layer related data. The physical layer is responsible for data modulation, transmission and reception, clear channel assessment (CCA) channel energy monitoring (energy detect, ED), and link quality indicaTIon (LQI). The physical layer frame structure consists of a synchronization header, a physical layer header, and a physical layer payload, as shown in Table 1.
The sync header further includes a 32-bit preamble and an 8-bit frame delimiter. The preamble is used to provide synchronization of symbols or data symbols for data transceiving; the frame delimiter is used to identify the end of the sync domain and the start of data. The physical layer header includes a 7-bit frame length and a 1-bit reserved bit. The frame length defines the number of bytes of the physical layer payload. The physical layer payload is the frame content of the MAC layer.
The MAC layer defines its interface with the network layer, including the data service interface MLDE-SAP and the management service interface MLME-SAP provided to the network layer, and provides MAC layer data service and MAC layer management service. The MAC layer data service mainly implements data frame transmission; the MAC layer management service is mainly responsible for medium access control and error control.
The main functions of the MAC layer include the following aspects: (1) ZigBee coordinator generates network beacons (2) devices synchronize with beacons
(3) Support node join or exit operation
(4) The channel access mode uses the collision avoidance carrier detect multiple access (CSMA-CA) mechanism (5) to establish and maintain the protection slot mechanism (6) to provide security support for the device.
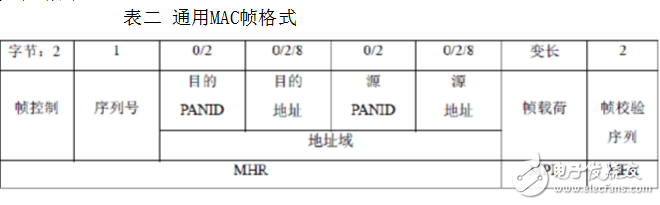
The MAC frame format consists of three basic parts: the MAC frame header, the MAC frame payload, and the MAC frame trailer. Different types of MAC frames have the same header and end of the frame, except that the MAC frame payload is different. The general MAC frame format is shown in Table 2.
The network layer defines the interface between it and the application layer, including the data service interface provided to the application layer.
NLDE-SAP and the management service interface NLME-SAP provide both network layer data services and network layer management services. The network layer is mainly responsible for the establishment of the topology and the maintenance of the network. The specific functions are as follows: (1) Initialize the network, that is, establish a new network including the coordinator, router and terminal equipment. (2) Use when the device is connected and disconnected. Mechanisms
(3) Discovery of one-hop neighbor nodes and storage of related node information
(4) ZigBee coordinator and router assign short addresses to newly joined nodes
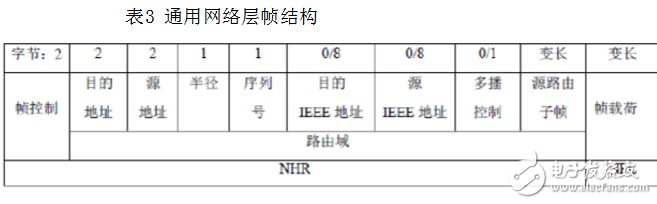
(5) Ensure that the MAC layer works normally, and provide a suitable service interface for the application layer. The network layer frame structure includes a network layer header (NHR) and a network layer payload (NPL), where the network layer frame The header field is composed of a frame control domain, a destination device address, a source device address, a broadcast radius, and a broadcast sequence number. The structure of the general network frame is shown in Table 3.
The ZigBee application layer is the highest layer in the protocol architecture. It consists of the application layer support sublayer (APS), ZigBee device object (ZDO), and ZigBee application framework (AF). The Application Support Sublayer (APS) defines the interface between the network layer and the application layer. One interface is the data entity service access interface APSDE-SAP used by ZDO and the manufacturer-defined application object, and the other is the management service access interface. APSME-SAP. The main role of APS is to maintain binding tables and pass information between bound devices. ZDO is located between the Application Layer Framework (AF) and the Application Support Sublayer (APS) to meet the common needs of all application operations in the protocol. The role of ZDO includes: device discovery and service discovery; defining a device type, such as defining a device as a ZigBee coordinator or a ZigBee terminal device; and constructing and storing a binding table according to a binding request to implement binding management. The ZigBee Application Framework (AF) is an environment in which application objects reside. There are up to 240 application object endpoints. Application objects send and receive data through APSDE-SAP, and application objects are managed through the ZDO public interface.
When the ZigBee protocol stack is running, the data frame is processed as follows: when the device initiates communication, the data is transmitted from top to bottom, passing through the application layer, the network layer, the MAC layer, and the physical layer in turn, after being processed by the physical layer. , transmitted through the wireless module modulation of the hardware. When receiving, the received information is first demodulated by the wireless module, and then transmitted according to the physical layer, the MAC layer, the network layer, and the application layer, and the information frame is decomposed.
Single Led,Monochrome Led Display,Small Single Led Light,Single Led Light
ShenZhen Megagem Tech Co.,Ltd , https://www.megleddisplay.com