The so-called digital television is to convert, quantize and encode a traditional analog television signal into a digital signal represented by a binary number, and then process, transmit, store and record various functions. The use of digital technology not only enables various TV devices to achieve higher technical performance than the original analog devices, but also has new functions that analog technology cannot achieve, making TV technology enter a new era.
This article refers to the address: http://
Compared with analog TV, digital TV has the following characteristics and advanced features: 1) higher definition, better audio effect and stronger anti-interference ability; 2) more reasonable and effective use of various spectrum resources. Digital TV adopts data compression coding technology, and the transmission channel bandwidth is greatly reduced compared with analog TV. The 8MHz channel transmitting an analog TV program can transmit 4~6 sets of digital TV programs at the same time; 3) The signal transmission power is reduced, and the output signal is stable. Reliable, easy to eliminate image distortion, and the output signal is easy to store; 4) Digital TV output signal is scalable, scalable and operability, easy to transmit in various communication channels or cable TV channels.
A complete digital TV system, like the analog TV broadcasting system, is also composed of three major links: program source, broadcast and reception. The specific structure is shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the digital television system mainly consists of source codec, program stream and transport stream multiplexing/demultiplexing, channel transmission, channel codec, modulation and demodulation and the like. The M88DD2000 launched by Hi-Tech is a high-performance demodulator for China's national standard terrestrial digital TV. It completes the functions of demodulation and decoding of the receiving end of the digital TV system, and has excellent system performance in fixed, mobile or portable. Its main application areas include: ground set-top boxes, digital TV all-in-ones, mobile and handheld TVs.
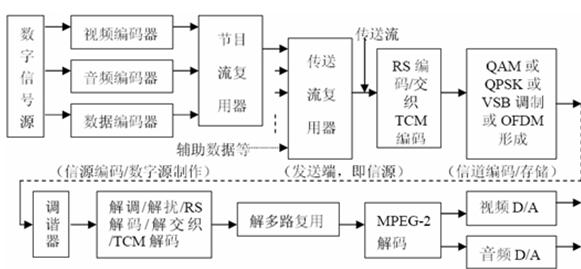
Figure 1 The composition of the digital TV system
1. Main features and advantages of M88DD2000:
1. In line with the national standard GB20600-2006 standard;
2. Support single-carrier and multi-carrier signal demodulation;
3. Support all demodulation modes defined by the national standard GB20600-2006;
4. Support 6/7/8MHz signal bandwidth;
5. Embedded high-performance 10-bit digital-to-analog converter for direct sampling of intermediate frequencies (4.57MHz and 36.167MHz);
6. Embedded special pulse interference cancellation module for filtering impulse noise, effectively improving the anti-pulse interference capability;
7. Strong ability to select adjacent channels, greatly improving the performance of lead selection;
8. Strong anti-channel delay expansion capability;
9. Embedded special MCU, which can lock indication, signal quality, device state control and scheduling, which greatly simplifies the product development process;
10. Support automatic mode detection and parameter recovery and update;
11. Embedded power management module, can support three power modes: single 3.3V, 3.3V and 1.8V or 3.3V and 1.2V power supply;
12. Low power consumption design, reducing power consumption and improving system stability;
13.100pin LQFP small package.
2, M88DD2000 internal block diagram and working principle
The block diagram of the internal function module of M88DD2000 is shown in Figure 2.
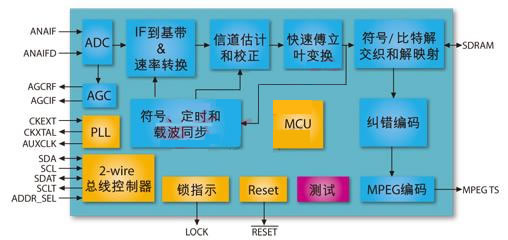
Figure 2: Block diagram of the internal functional blocks of the M88DD2000.
3, the working principle of each module
ADC
The M88DD2000 includes a high-performance 10-bit wide ADC for direct sampling of the IF. The supported IF frequencies are 4.57MHz and 36.167MHz with bandwidths of 6MHz, 7MHz, and 8MHz.
AGC
The M88DD2000 has two analog AGC (Automatic Gain Control) outputs, one for automatic gain control of the RF and the other for automatic gain control of the IF. The AGC loop generates the Pulse Width Modulator of the AGC by comparing the magnitude between the sampled signal and the AGC reference value. The rate of the PWM is adjusted based on the level of the input signal.
Front end module
The main functions of the Front End include: DC removal, impulse noise removal, digital AGC, IF to baseband down conversion, and interpolation filtering and rate conversion. The effect of DC removal is to compensate for gain imbalance, phase shift deviation, and DC offset for both I/Q after AD conversion. Impulse noise removal compares the amplitude of the sampled signal with a pre-set threshold. If the amplitude of the sampled signal is above the threshold for a continuous period of time, then the presence of impulse noise is considered to be filtered. The function of the digital AGC is to compensate the power of the digital signal after filtering, and to adjust the average power of the input signal within a certain period to adjust it to a preset reference value. The down-conversion function of the intermediate frequency to the baseband is to multiply the digital local carrier signal by the sampled input signal, and filter the high-frequency component to obtain the useful signal of the baseband; the interpolation filtering and the rate conversion are based on the symbol rate and the timing recovery module output. The control signal extracts the signal to obtain a sampled signal that is consistent with the symbol rate.
FFT
The FFT module performs a fast Fourier transform. The FFT module is triggered by the symbol timing and carrier synchronization module. On multi-carrier, the FFT performs a transform from the time domain to the frequency domain. In the case of a single carrier, after completing the FFT transform, an IFFT transform is performed to transform the signal into the time domain again, and the pilot information can be extracted by using the result of the FFT transform.
Channel estimation and correction
The channel estimation module performs time domain correlation with the PN sequence of the received signal using the local PN sequence, thereby completing channel estimation and correction, and determining the frame start position of the multicarrier or single carrier.
Symbol, timing and carrier synchronization
The symbol synchronization module dynamically adjusts to ensure the correct starting point of the frame body symbol so that the FFT operation can be performed correctly or the single carrier frame volume data block can be extracted.
The timing synchronization module is an all-digital clock recovery circuit that compensates for sampling time variations due to crystal or external clocks.
The carrier synchronization module is used to track and compensate for frequency errors caused by inconsistent frequency at the transceiver end.
Symbol/bit deinterleaving and demapping.
The deinterleaving module performs deinterleaving on the data symbols, but is the inverse of the originating interleaving.
The demapping module de-maps the data symbols according to the location of the constellation.
FEC (LDPC and BCH error correction decoding)
The input after demapping is sent to LDPC decoding and BCH decoding, and the error generated in the transmission is detected and corrected according to the indication of the system information, and finally the demodulated and decoded data stream is formed.
MPEG Formatter (MPEG Formatter)
The decoded data stream is transmitted to the MPEG output interface according to the interface data format of the MPEG-TS, and can be sent to the image decoding chip or the main controller chip of the back end. The M88DD2000 supports MPEG-TS output data interfaces including: parallel port, serial port and MPEG-TS universal interface, which can support up to 61.44MHz instantaneous data rate.
I2C interface
The M88DD2000 has two I2C interfaces, one for control and setup of the M88DD2000 and the other for relaying the tuner control by the master chip.
Embedded MCU
The M88DD2000 embeds a high-performance MCU to control and schedule all internal modules, as well as the acquisition and indication of related signal quality.
4, typical application
Thanks to its high integration and versatile interface design, the M88DD2000 can be used with only a few external components, and a universal tuner and source decoder form a complete national standard converged set-top box supporting multi-carrier and single-carrier. Receiving system.
The M88DD2000 provides a complete interface to the tuner and source decoder, as shown in Figure 3.
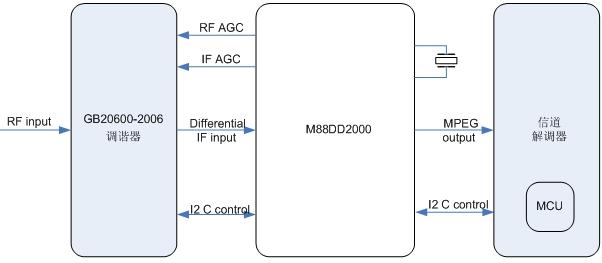
Figure 3: Typical application of the M88DD2000.
The interface between the M88DD2000 and the national standard terrestrial digital tuner mainly includes: RF AGC output, IF AGC output, I2C repeater interface, and differential input for transmitting the national standard IF signal. The reference levels of the RF AGC and IF AGC can be changed by writing to the register, while the polarity of the AGC PWM output can be defined by the user. The IF signal to the M88DD2000 is a differential input (IF+, IF-) analog signal. I2C is the interface that M88DD2000 sends to the tuner after relaying the MCU control signals in the channel decoder.
The interface between the M88DD2000 and the channel decoder has an MPEG TS interface and an I2C interface. The MPEG TS interface is a process in which data demodulated and decoded by the M88DD2000 is sent to a channel decoder for demultiplexing and decompressing images and sounds. The MPEG interface supports both parallel and serial interface modes with a maximum bit rate of 61.44M. I2C is connected to the MCU in the image decoder to transmit the system control signals generated by the MCU to the M88DD2000 and the tuner.
Summary of this article
M88DD2000 is a national standard, high-performance demodulation chip launched by China Technologies for the digital terrestrial TV market in China. It adopts a highly integrated system architecture and excellent digital processing algorithms to provide customers with lower power consumption and better. Performance solution.
FRP Pipe,GRP Pipe,FRP Products
Water Treatment Plant Co., Ltd. , http://www.nsfrptank.com