MAC is the media intervention control layer, which belongs to the lower layer of the data link layer in the OSI model. It defines how data frames are transmitted over the medium. In a link that shares the same bandwidth, access to the connected medium is "first come, first served." Physical addressing is defined here, and the logical topology (the path through which the signal passes through the physical topology) is also defined here. Line control, error notification (not corrected), frame delivery order, and selectable flow control are also implemented at this sublayer.
Type of MAC protocolThe core problem of multiple users, multiple access is: How to adopt some coordination mechanism, that is, what kind of MAC protocol, when multiple users compete for one channel. For example, two extreme MAC protocols, one is completely free, the user is free to send, but to solve a problem is what to do after the collision, one is completely sorted, each user is specified with detailed rules to send, Receive the package. However, this is actually not possible because the MAC protocol mainly determines the throughput, delay, and other performance of the communication. Therefore, this block is very important and is a combination of multiple methods. The MAC protocol is mainly divided into the following three categories.
1. Fixed allocation channel. The channel can be basically divided into frequency division, time division, code division, and space division. Each user is fixedly allocated a channel. This method is highly real-time, but it is wasteful. Mainly for voice. Such as FDMA (telephone), TDMA (GSM), CDMA.
2. Randomly allocate channels. . Mainly for data. For example, ALOHA, CSMA is a typical example of random assignment.
3. Assign channels on demand. According to the requirements of the users, channels are allocated according to requirements. For example, 802.16 allocates channels according to requirements. Mainly face-type multimedia.
MAC frame formatThe basic format of the MAC frame is shown in the following figure:
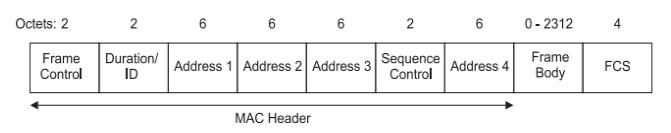
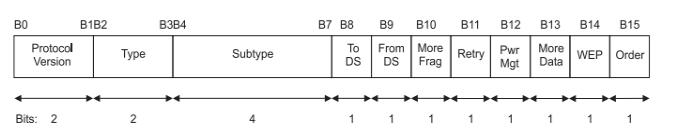
-ProtocolVersion: currently 0
-Type: The frame category has the following three types, and each category has some subcategories (see Subtype).
00: Management frame (ManagementFrame)
01: Control frame (ControlFrame)
10: Data frame (DataFrame)
11: Reserved unused
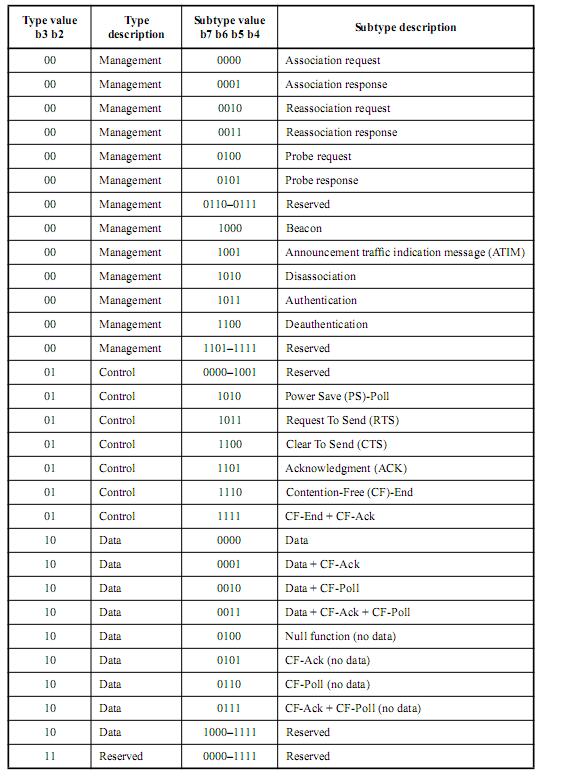
-Subtype: The frame subcategory, together with the Type, determines the type of a frame, as shown in the following table.
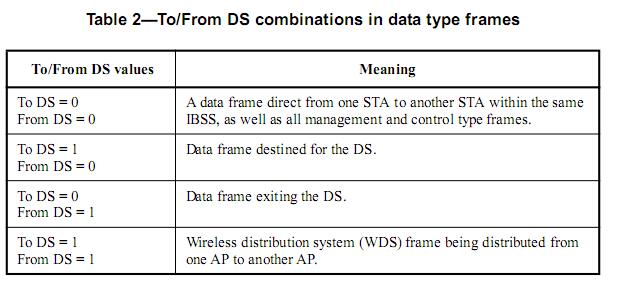
-ToDS/FromDS: Indicates whether the frame destination is DS (distributed system), which can be simply understood as whether it is sent to/from AP.
-Morefragments: Indicates if there are any shards (remove the last shard)
-Retry: Indicates whether the current frame is a retransmission frame. The receiver will delete the duplicate frame after receiving it.
- Powermanagement: Indicates the power management mode of the STA. 1 indicates that the STA enters the Power-Save mode after the data exchange is completed. The STA is always 0 for the AP.
-Moredata: Instructs the AP to perform frame buffering (from DS) for STAs entering the power saving mode.
-WEP: Indicates whether the framebody is encrypted using WEP
-Order: indicates that StrictlyOrdered will be transmitted
2, other fields-DuraTIon/ID: Can be used in the following three scenarios

@1DuraTIon, the 15th position is 0, used to set the NAV, the value represents the number of microseconds expected to use the medium
@2 In the CFP frame, the 14th position is 0, the 15th position is 1, the other value is 0, and the field value is 32768, so that other STAs that have not received the Beacon frame announce no contention period.
@3 In the PS-Poll (Power Save-Poll) frame, the 14th and 15th bits are set to 1 at the same time, and the STA awake from the power saving mode sends an AID (Association Identifier) ​​to obtain the cache frame in the AP.
-Address: There are the following types. The address type determines which address fields to use. There are usually three, SA, DA, and BSSID.
BSSID, basic service set identifier
DA, destination address
SA, source address
RA, receiver address
TA, sender address
-SequenceControl: contains two subfields, a 4-bit slice number (FragmentNumber) and a 12-bit sequence number (SequenceNumber)
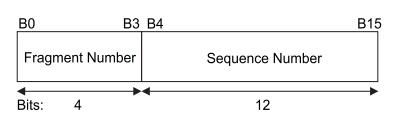
The modulus of sequence number 4096 starts from 0 and adds 1 to each upper packet.
If the upper packet is fragmented, all frame fragments are numbered in the same order.
For retransmission frames, the sequence number is unchanged
-FrameBody: The frame body is also called the data field (Datafield), used to pass the upper layer payload (Payload), which can be 0.
- FCS: Frame check sequence, using cyclic redundancy check (CRC) code, the calculation range includes all fields and frame bodies in the MAC header.
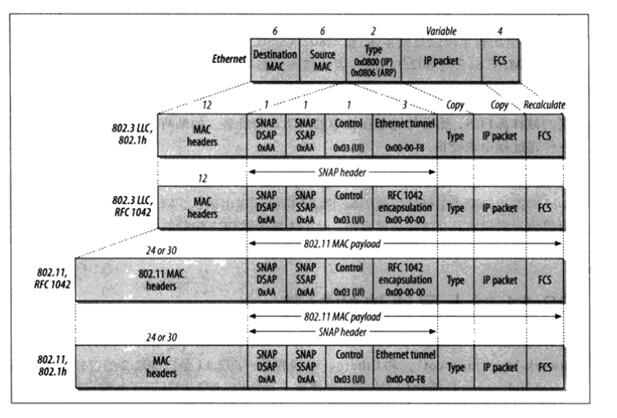
3, frame body dataUnlike Ethernet, 802.11 FrameBody encapsulates different types of network protocols with 802.2 logical link control (LLC).
Available in two packages: RFC1042, 802.1H
The following figure shows the IP encapsulation in 802.11.
General modification
You need to contact the manufacturer according to the MAC chip model to get the corresponding firmware flashing tool, and the MAC address file. The MAC address is a valid segment to be purchased from the IEEE Alliance, and is unique. If there is a duplicate, the IP address is duplicated. An error caused the computer network access of the same MAC address to be abnormal.
Modify the MAC address under Unix/Linux system
Enter the save MAC information file
Under the graphical interface Alt+Ctrl+Space→Open the command line terminal→
Method 1, enter: ifconfig
Method 2, enter: ifconfig|grep "inet"|cut-c0-36|sed-e's/[a-zA-Z:]//g'
Method 3, enter: hostname-i
Method 4, enter: netstat-r
Method 5, enter: cat / etc / resolv.conf
→Display related network data
Where inetaddr is the ip address and HWaddr is the host's HardwareAddress or MAC address.
Modify MAC
Method 1, modify the MAC method: add ifconfigeth0hwetherxx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx(MAC) in the network in /etc/rc.d/init.d/ and then restart it will find that the network card address is already xxxxxxx It is.
Method 2, you can also add /sbin/ipconfigeth0hwetherMACaddr to /etc/rc.local.
China Changing Cabinet,Battery Cabinet,Battery Changer Cabinet,Battery Switch Cabinet, we offered that you can trust. Welcome to do business with us.
Changing Cabinet,Battery Cabinet,Battery Changer Cabinet,Battery Switch Cabinet
Shenzhen Hongjiali New Energy Co., Ltd. , https://www.hjlcharger.com