Low-voltage electrical appliances are the basic components of electric drive control systems and low-voltage power supply and distribution systems. Their performance directly affects the reliability, advancement and economy of the system, and is the basis of electrical control technology. Electromagnetic low-voltage electrical appliances are used in large quantities and types in electrical control circuits, but their working principles and structures are basically the same. Most of them are composed of three main parts: contact, arc extinguishing device and electromagnetic mechanism.
1. The composition and working principle of the electromagnetic mechanismThe role of the electromagnetic mechanism is to convert electromagnetic energy into mechanical energy and drive the closing or opening of the contact to complete the control function of the on-off circuit (ie, the action of the contact is driven by the generated electromagnetic attraction).
The composition of the electromagnetic mechanism: attracting the coil, the iron core (static iron core) and the armature (moving iron core). The electromagnetic mechanism generally consists of a core, an armature and a coil. According to the current type passing through the coil, there are an alternating electromagnetic mechanism and a direct current electromagnetic mechanism; according to the shape of the electromagnetic mechanism, there are two types of E-shaped and U-shaped; according to the movement form of the armature, there are two types of snap-on and direct-acting.
The structure of the electromagnetic mechanism: according to the movement of the armature can be divided into direct-acting and snap-on.
The working principle of the electromagnetic mechanism: the coil passes current, generates a magnetic field, forms a loop through the iron core, the armature and the air gap, generates electromagnetic force, and sucks the armature toward the iron core.
As shown in Figure 1-1. Figure 1-1 (a) is the snap-on core with the armature rotating along the corners, Figure 1-1 (b) is the snap-on core with the armature rotating along the axis, and Figure 1-1 (c) is the double E of the linear movement of the armature Straight-moving iron core.
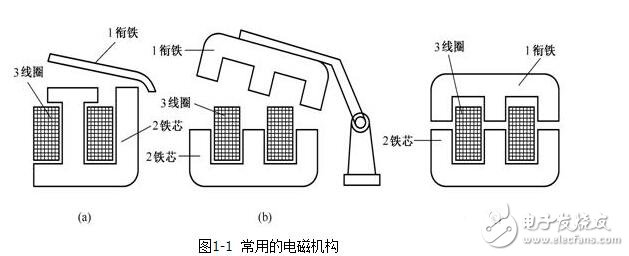
The core of the AC electromagnetic mechanism and the DC electromagnetic mechanism are different. The core of the DC electromagnetic mechanism is an integral structure to increase the magnetic permeability and enhance the heat dissipation; the core of the AC electromagnetic mechanism is formed by stacking silicon steel sheets. The purpose is to reduce the eddy current generated in the iron core and heat the iron core. In addition, the core of the AC electromagnetic mechanism has a short-circuit ring to prevent the armature from vibrating when the current is zero-crossing (lag 90°).
Principle: When there is working current in the coil, the energized coil generates a magnetic field, so the electromagnetic suction overcomes the reaction force of the spring to close the armature and the iron core, and the corresponding contact action is driven by the connecting mechanism.
Function: Convert the current in the coil of the electromagnetic mechanism into electromagnetic force, drive the contact action, complete the control function of the on-off circuit, and convert the electromagnetic energy into mechanical energy.
Attracting coil
The attraction coil acts to convert electrical energy into magnetic field energy. According to the type of the input current, it is divided into DC coil and AC coil.
For the DC electromagnet, since the core does not generate heat, only the coil generates heat, so the electromagnetic coil of the DC electromagnet is made of a high and thin elongated type without a coil bobbin, so that the coil and the core are in direct contact with each other to facilitate heat dissipation.
For the AC electromagnet, since the core has hysteresis and eddy current loss, the coil and the iron core are both heated, so the electromagnetic coil of the AC electromagnet is provided with a skeleton, so that the iron core is isolated from the coil and the coil is made short and thick, so that the coil is short and thick. Doing heat dissipation for the core and coil.
Separating magnetic ring of AC electromagnet
Split magnetic ring (also called short circuit ring): For single-phase AC electromagnetic mechanism, a copper magnetic ring is generally placed on the end face of the core to improve the working condition.
Short-circuit ring working principle: the magnetic flux of the electromagnetic mechanism is alternating, and the electromagnetic suction is proportional to the square of the magnetic flux. When the magnetic flux is zero, the suction force is also zero. At this time, the armature is pulled open under the action of the spring reaction force. When the magnetic flux is greater than zero, the suction force increases. When the suction force is greater than the reaction force, the armature is sucked again, and the armature generates strong vibration and noise. Vibration can shorten the life of the appliance. Therefore, in order to eliminate vibration, the single-phase AC electromagnetic mechanism must be equipped with a magnetic separation ring.
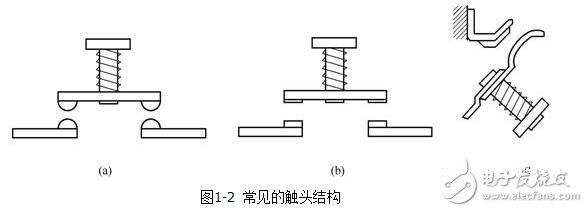
The contacts are used to turn the circuit on or off, and there are many types of structures.
(1) According to its contact form: according to its contact form, it is divided into three types: point contact, line contact and face contact.
As shown in Figure 1-2. Figure 1-2 (a) is a point contact bridge contact, Figure 1-2 (b) is a surface contact bridge contact, Figure 1-2 (c) is a line contact finger contact. The point contact allows a small current to pass, and the surface contact and line contact allow a large current to pass.
(2) According to the control circuit: the control circuit is divided into main contact and auxiliary contact. The main contacts are used to turn the main circuit on or off, allowing a large current to pass. The auxiliary contacts are used to switch the control circuit on or off, allowing only a small current to pass.
(3) According to the original state: according to the original state is divided into normally open contacts and normally closed contacts. When the coil is not charged, the moving and static contacts are separated as normally open contacts; when the coil is not charged, the moving and static contacts are closed, which is called normally closed contacts.
3, arc extinguishing systemThe concept of arc: The arc is actually a discharge phenomenon caused by the gas between the contacts under the action of a strong electric field, which generates high temperature and emits strong light, burns the contacts, and prolongs the cutting time of the circuit. In severe cases, it may cause fire or other Accidents, therefore, appropriate measures should be taken in the appliance to extinguish the arc.
Classification of arcs: The arc is divided into a DC arc and an AC arc. The AC arc has a natural zero crossing, so the arc is easier to extinguish.
Remark: When breaking the circuit in the atmosphere, if the current of the circuit being interrupted exceeds a certain value (the value is between 0.25-1A according to the contact material section), it is added to the contact gap after the breaking (or When the voltage across the arc gap exceeds a certain value (between 12-20V depending on the material of the contact), an arc is generated in the contact gap.
Arc generation: When the switching device cuts off the current circuit, the voltage between the contacts is greater than 10V, and when the current exceeds 80mA, a blue light column, that is, an arc, is generated between the contacts. The arc generates high temperature and has strong light, which can burn the contacts and prolong the cutting time of the circuit. In severe cases, it can cause accidents or fires.
The hazard of the arc:
1. Extend the time to cut off the fault;
2. The high temperature causes the electrical insulation material near the arc to burn out;
3. The formation of arcing causes a short circuit in the power supply.
The generation of electric arc: all kinds of contact electric appliances are opened and closed through the contacts to open and close the circuit. (http://Copyright) When the contact is connected to the circuit, there is a contact resistance, which causes the contact to heat up. When the contact breaks the circuit, the gas is released due to the action of the hot electron emission and the strong electric field, thereby generating an arc at the moment of breaking.
Arc-extinguishing measures: blowing arc, drawing arc, long arc cutting short arc, multi-break arc extinguishing, using medium arc extinguishing, improving contact surface material.
Common arc extinguishing methods: electric power arc extinguishing, magnetic blow arc extinguishing, narrow slot arc extinguishing and grid arc extinguishing.
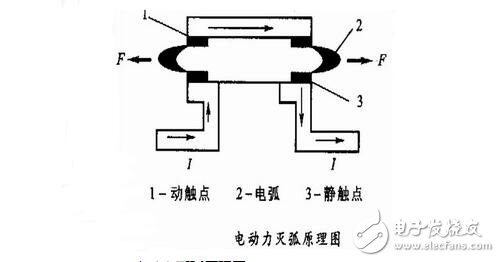
Method of arc extinguishing:
(1) Mechanical arc extinguishing: The arc is rapidly elongated by a machine for switching the circuit.
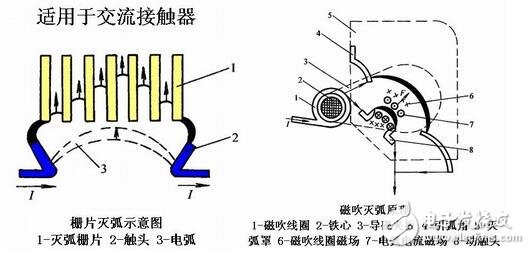
(2) Magnetic blowout: Under the action of a magnetic force generated by a magnetic blow coil in series with the contact, the arc is elongated and blown into an arc chute made of a solid medium, and the arc is cooled and extinguished.
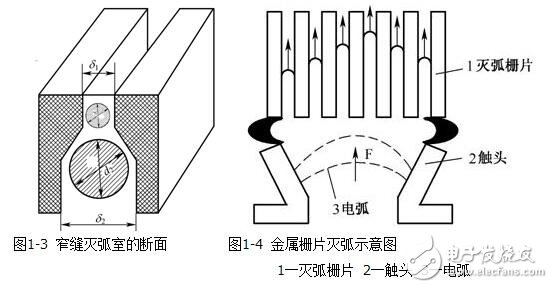
(3) Narrow-slit arc extinguishing: Under the action of the magnetic field and electric field force formed by the arc, the arc is elongated into the narrow slit of the arc-extinguishing cover, divided into several segments and quickly extinguished, as shown in Figure 1-3. This method is mainly used in AC contactors.
(4) Arc extinguishing of the grid: When the contacts are separated, the generated arc is pushed into a group of metal grids by the electric field force and divided into several sections, and the metal sheets insulated from each other are equivalent to the electrodes, so that there are many yin and yang Extreme voltage drop, for the AC arc, the arc can not be maintained and extinguished when the arc crosses zero. As shown in Figure 1-4, the common grid of the AC appliance is arc extinguished.
Cable Gland,Power Cable,Cable Clips,Cable Organizer
Changshu Herun Import & Export Co.,Ltd , https://www.herunchina.com